Certifications
AIEX – YOUR PARTNER IN TRAINING, QUALIFICATION AND CERTIFICATION!

Technical Safety in Electrotechnology
Forms: Application Form; Acceptance Criteria; Complaint or Appeal Form
Policy: Impartiality Policy
Procedures: Complaint or Appeal Procedure; Certification/Recertification Procedure
Download Documents
Technical Safety in Electrotechnology - 2nd Group
The second group belongs to the students of professional schools and/or university of electrical engineering, line controllers, welders, electronic technicians, all low-skilled electricians with working experience not less than 1 year in the relevant profile.
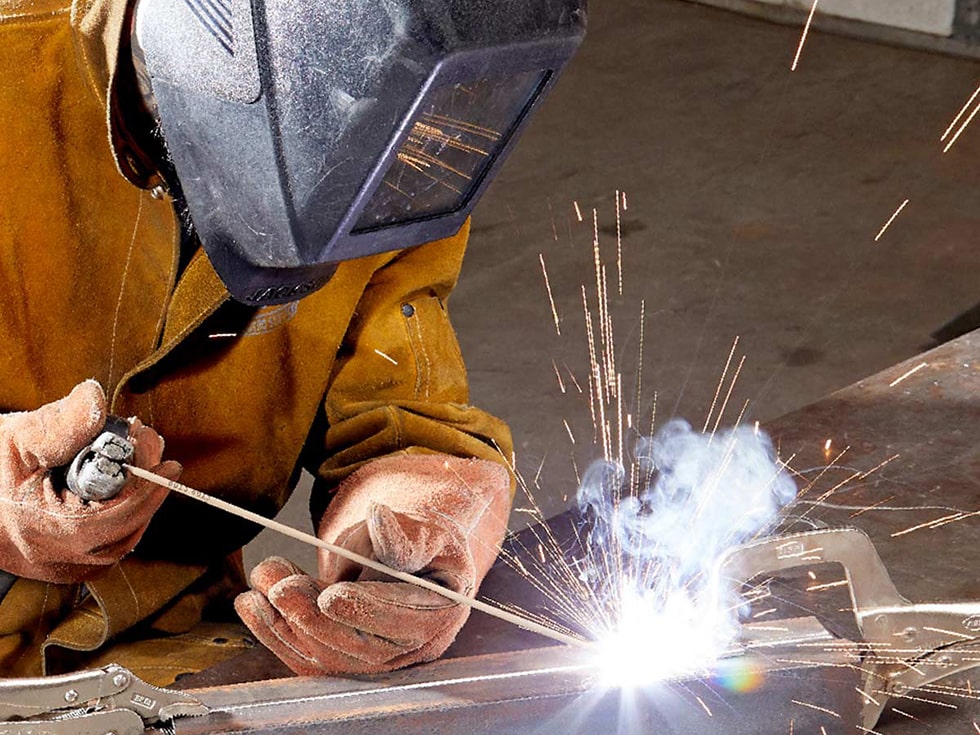

Manual Metal Arc Welding (MMAW)
Shielded metal arc welding, also known as manual metal arc welding, or informally as stick welding, is a manual arc welding process that uses a consumable electrode covered with a flux to lay the weld.

Metal Inert Gas Welding
(MIG Welding)
A welding process in which an electric arc forms between a wire electrode and the workpiece metal, which heats the workpiece metal, causing them to melt and join. The used shielding gas, is an inert gas (Argon or Helium).
Read More
AIEx is the Official ÖSD Examination Centre in Albania
ÖSD is a state-approved testing and assessment system for German as a foreign and second language, since 2014 officially provided by AIE in Albania.
Register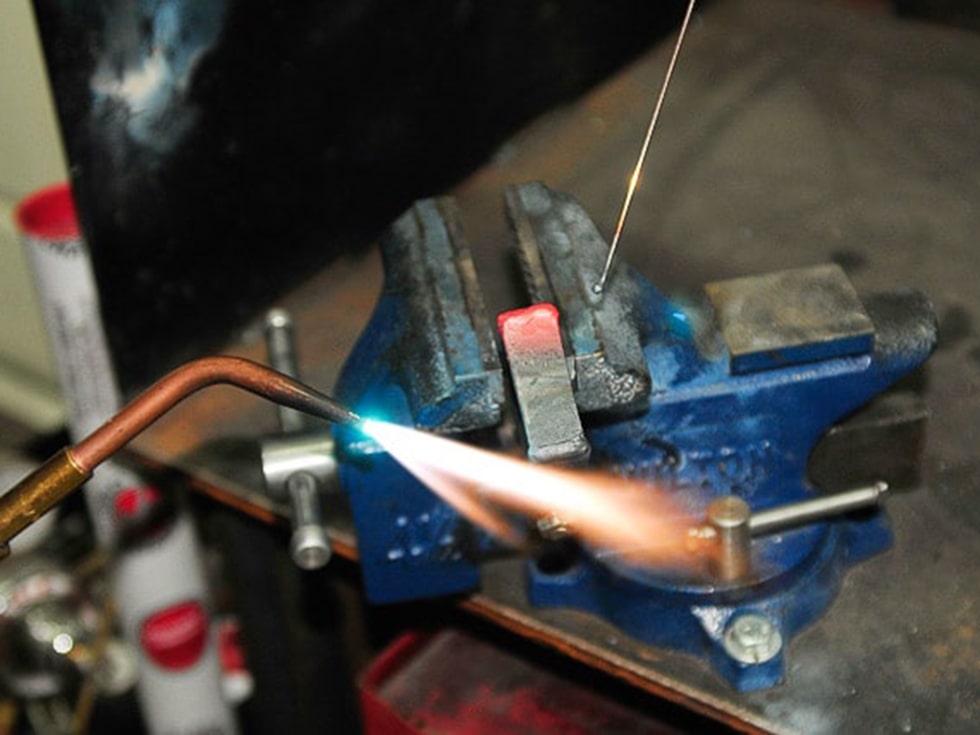
OXY - Fuel Welding
Oxy-fuel welding, commonly called oxy-acetylene welding, or gas welding and oxy-fuel cutting, are processes that use fuel gases and oxygen to weld and cut metals.
Read More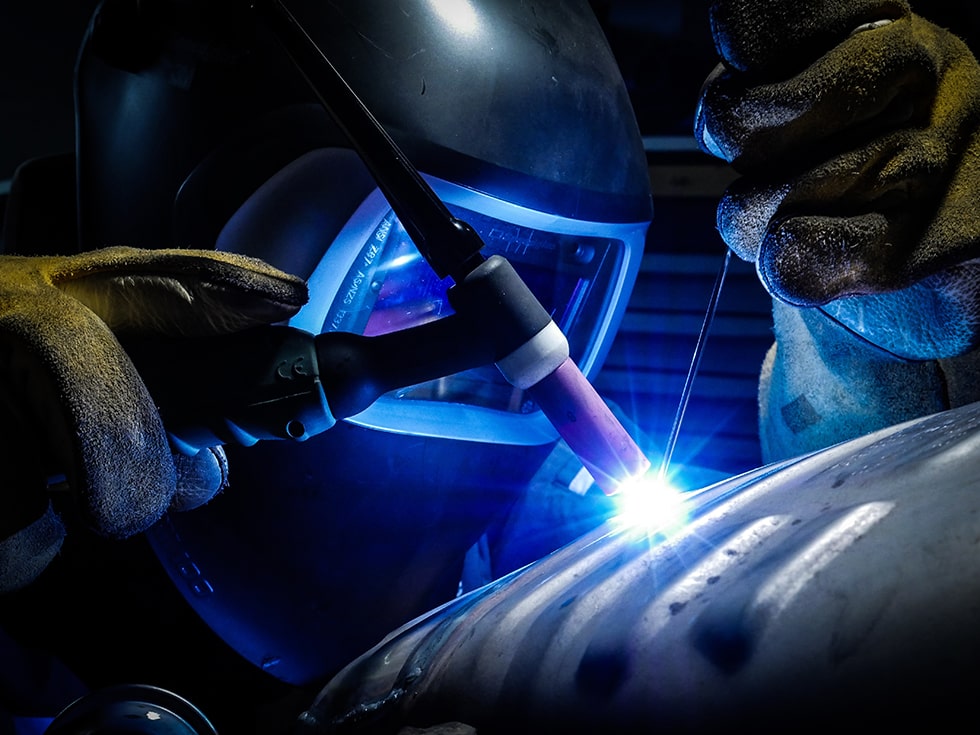
Tungsten Inert Gas Welding
(TIG Welding)
Tungsten gas arc welding, also known as tungsten inert gas welding, is an arc welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld.
Read More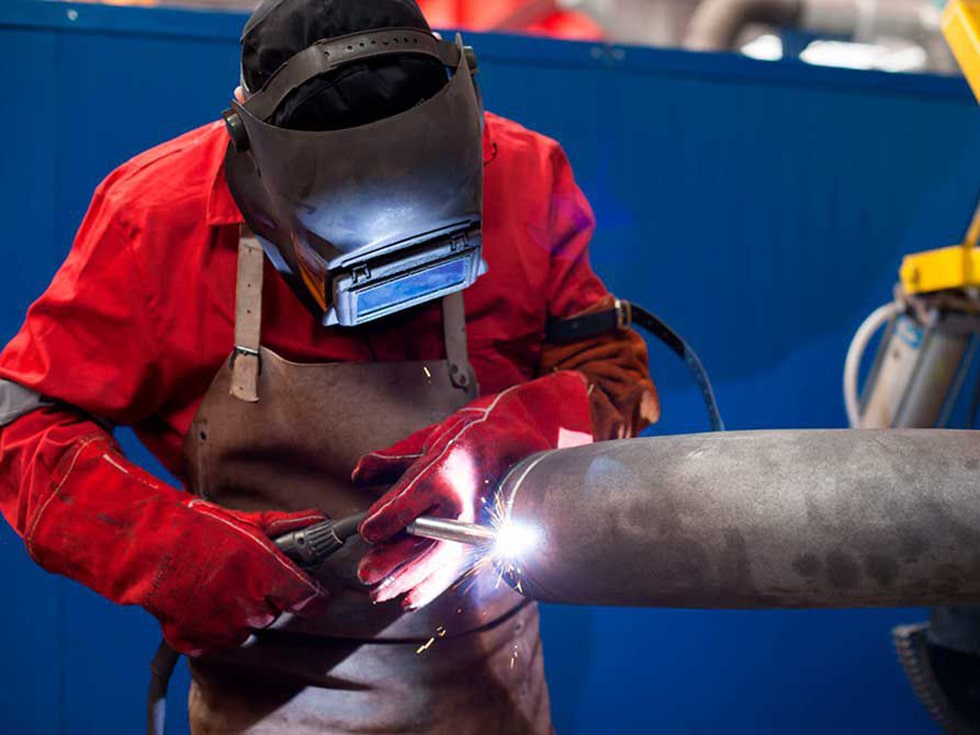
Metal Active Gas Welding
(MAG Welding)
A welding process in which an electric arc forms between a wire electrode and the workpiece metal, which heats the workpiece metal, causing them to melt and join. The used shielding gas, is an active gas, usually a mixture of CO2 and Argon
Read More
International Welding Specialist
IWS is a training programme with an internationally recognized diploma, developed from the International Welding Institute IIW, as part of the qualification scheme for the welding coordinator according to EN ISO 14731.
Read More